The Natural Hip Joint
The hip joint plays an important role in movement and maintaining balance. It also supports weight while we are standing, sitting, running or walking.
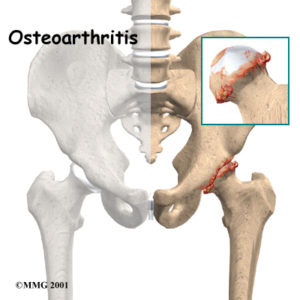
The hip is a ball and socket joint. It is made up of two parts. The first is the hip socket and the other is the thigh bone called the femur. A smooth material called cartilage lines the socket, allowing the ball to move smoothly inside the socket. In a diseased hip, the cartilage wears out resulting in bone to bone contact that can be painful.
Who May Need Hip Replacement Surgery?
Arthritic Hip
If you have severe hip pain that is limiting your mobility and affecting your daily functions, you may benefit from hip replacement surgery.
The following three are the most common causes of joint damage due to arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis – a disease which involves the wearing away the normal smooth joint surfaces. This results in bone-on-bone contact, producing pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – The body’s immune system attacks and destroys the synovial lining covering the joint capsule, the protective cartilage and the joint surface. This causes pain, swelling, joint damage and loss of mobility.
- Trauma Related Arthritis – resulting from damage to the joint from a previous injury. It also results in joint damage, pain and loss of mobility.
Deformity Correction
If you have hip deformities like developmental dysplasia, leg length discrepancy etc., hip replacement may help to restore normal anatomy and function.
Femoral Neck Fractures
Some severe form of hip fractures are best treated with hip replacement surgery.
Avascular Necrosis (AVN)
AVN is a disease in which the head of the femur dies due to lack of blood circulation and is unable to support the weight of the body. If you have a hip collapse due to AVN, hip replacement is a good option to consider.
Reconstruction
Hip replacement can help reconstruct the limb in cases of severe bone loss due to cancer or tumours.
What is Hip Replacement Surgery?
Total hip replacement (THR) is the replacement of the ball and socket of the hip joint with implants. There are two main components used in total hip replacement. The acetabular shell replaces the hip socket. The femoral stem replaces the worn-out top of the femur.

How is Hip Replacement Surgery Performed?
There are generally 6 steps to the hip replacement surgery. These include the following:
Step 1 – Exposure
After making an incision, the hip joint is exposed.
Step 2 – Head Resection
Your surgeon will remove your femoral head from your acetabulum (hip socket). This is done so the surgeon has clear access to the hip joint.
Step 3 – Bone Preparation
The damaged surfaces of the femoral head and acetabulum are then removed and the underlying bone is prepared to accept the artificial hip implants.
Step 4 – Implant Insertion
The new hip implant components are placed into the femur and acetabulum.
Step 5 – Implant Trial
Once all the implant components are in place, your surgeon will place the new femoral head into the acetabular component and check that the movements are full, smooth and stable.
Step 6 – Closure
Finally, the surgeon will close the incision (wound), dress it, and ensure you get bed rest.
After a special instrument shapes the hip socket, a metal shell is placed into the socket. A ceramic liner is then inserted into the shell which provides the bearing surface.
Finally, a ceramic ball is placed onto the metal stem which is placed into the new socket.
Your Hip Replacement Options
There are many options possible in hip replacement surgery. There are different types of bearing options and stem options available.
Bearing Options:
The bearing is where the ball and cup liner meet. This is where the motion of the hip comes from, because the two surfaces move against each other. Bearings can be made of metal, ceramic or polyethylene (medical grade plastic). The bearing is critical in the performance of your implant. It affects your hip’s mobility, flexibility and range of motion, as well as how the implant will stand up over time and how stable it will be in your body.
Stem Options:
With multiple stem choices in various sizes and configuration, your surgeon will choose the implant that suits your natural anatomy.
Recovery After Hip Replacement Surgery
Generally, within 6 weeks after surgery, you may return to some activities, driving and work.
You should be able to return to most normal activities within a few months of the surgery, including climbing stairs, gardening and other low impact activities.